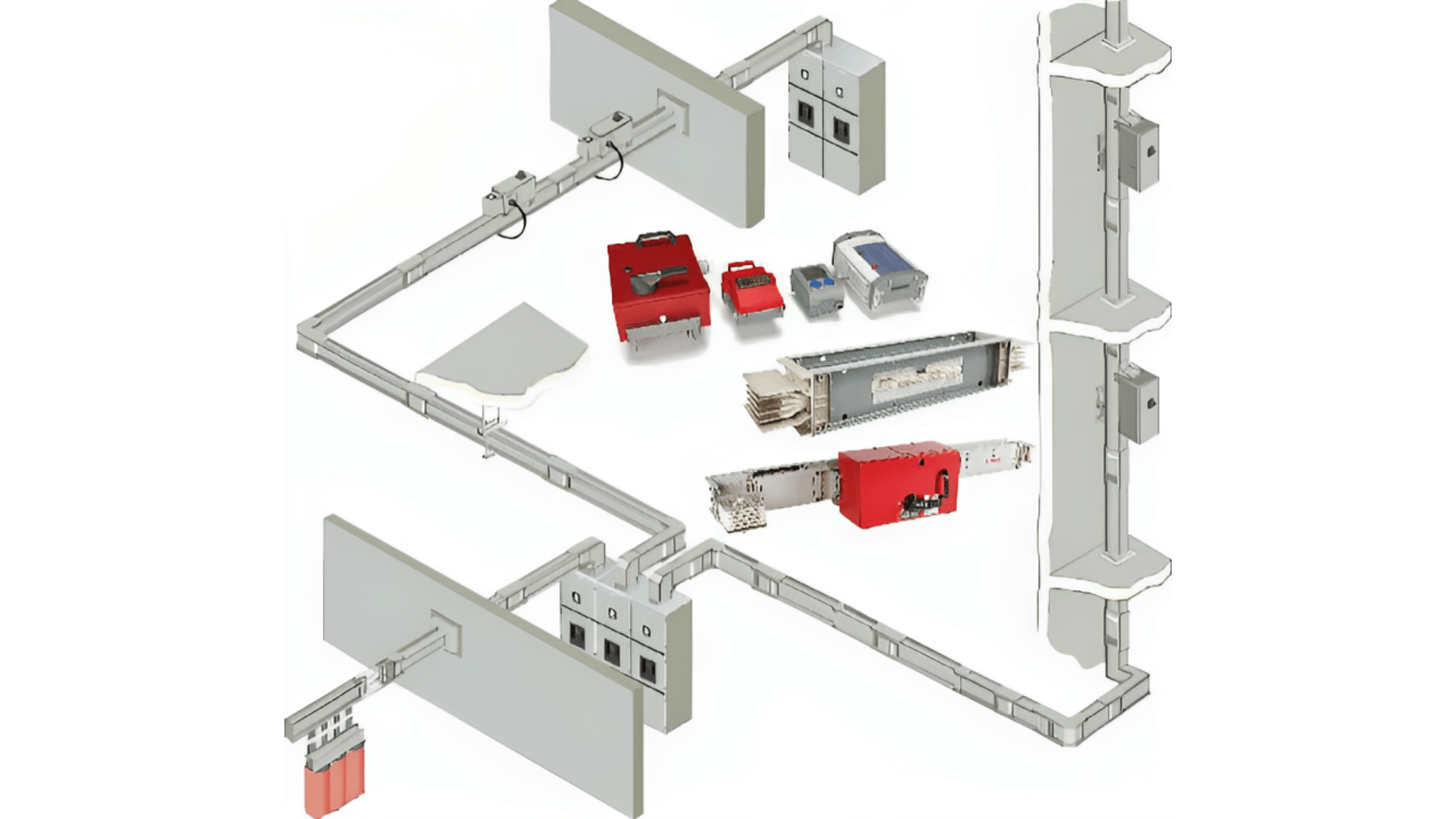
Bus Bar Tracking System (BBT)
A Bus Bar Tracking System (BBT) is a technology used in electrical power distribution systems to monitor, detect, and prevent issues related to busbars, which are critical components in the distribution of electrical power within a facility, substation, or industrial plant. A busbar is essentially a metal strip or bar (usually made of copper or aluminum) used to carry large amounts of current in electrical circuits. The Bus Bar Tracking System is designed to monitor the performance and health of busbars to avoid failures that could lead to system downtime, equipment damage, or even safety hazards.
Key Functions of a Bus Bar Tracking System (BBT)
- Real-Time Monitoring of Busbars
The BBT continuously monitors the status of busbars, tracking key parameters such as:- Current Flow: Measuring the amount of electrical current flowing through the busbar.
- Temperature: Monitoring the temperature of the busbar to detect overheating or excessive heating, which could indicate a potential failure.
- Voltage: Checking for voltage fluctuations or imbalances across the busbar.
- Mechanical Stress: Monitoring for any physical deformation or stress that could affect the busbar’s performance.
- Condition Monitoring and Diagnostics
The system provides diagnostic information that can be used to assess the condition of busbars, including:- Wear and Tear: Identifying signs of corrosion, oxidation, or other forms of degradation on the busbar.
- Loose Connections: Detecting if there are any loose connections or bad joints that could lead to high-resistance points and eventually cause overheating or failure.
- Insulation Health: Monitoring the condition of insulation materials used in the busbar to prevent short circuits and leakage.
- Fault Detection and Alarm Systems
The BBT system is equipped with fault detection capabilities:- Overcurrent Protection: Detects when the current exceeds the safe operating limits, triggering an alarm and activating protective mechanisms (such as circuit breakers).
- Overtemperature: If the busbar temperature rises above a safe threshold, the system will send alerts to operators for immediate attention.
- Short Circuit or Ground Faults: Identifies short circuits or faults in the busbar system, helping operators respond quickly to avoid damage.
- Data Logging and Reporting
- The system collects data over time, providing insights into the operational trends of busbars. This data can be used for long-term analysis, preventive maintenance, and performance optimization.
- Detailed reports are generated to identify potential issues before they cause significant problems, supporting predictive maintenance efforts.
- Remote Monitoring and Control
Many modern Bus Bar Tracking Systems can be integrated with centralized monitoring systems, allowing remote access and real-time control. This enables operators to monitor busbar conditions from control rooms or even remotely via mobile devices. - Preventive and Predictive Maintenance
By continuously monitoring the busbar’s parameters, the BBT system helps operators detect early signs of failure or degradation. This information can be used to schedule maintenance activities before an actual fault occurs, preventing unscheduled downtime and costly repairs.
Components of a Bus Bar Tracking System
- Sensors and Transducers
- Temperature Sensors: Thermocouples, RTDs (Resistance Temperature Detectors), or infrared sensors are often used to measure the temperature of the busbars.
- Current Transformers (CTs): These devices are used to monitor the electrical current flowing through the busbar.
- Voltage Sensors: Measure the voltage at various points along the busbar to detect any anomalies.
- Vibration or Mechanical Stress Sensors: These sensors help detect physical movement or stress on the busbars.
- Data Acquisition System (DAQ)
- The data from sensors is collected by a data acquisition system, which processes and transmits the data for analysis and monitoring.
- Control and Monitoring Units
- Centralized Monitoring System: This can be a computer system or software interface that continuously collects and processes data from the sensors. The system can issue alarms or notifications based on predefined thresholds.
- User Interface (UI): Allows operators to visualize data, monitor trends, and receive alerts. This can be either local or remote.
- Alarm System: The BBT system will trigger alarms if the busbar exceeds acceptable limits for current, temperature, voltage, or physical strain.
- Communication Network
- Data from the monitoring system is often transmitted over a secure communication network (e.g., wired or wireless), connecting sensors to the central control system. Common protocols include Modbus, Profibus, or Ethernet/IP.
Advantages of a Bus Bar Tracking System (BBT)
- Enhanced Safety
- Early detection of faults such as overheating, short circuits, or loose connections helps prevent electrical fires, equipment damage, and even injury or fatalities.
- Real-time monitoring provides operators with actionable data to make quick decisions in emergency situations.
- Preventive and Predictive Maintenance
- The system allows for predictive maintenance by identifying issues before they lead to system failures. This helps to reduce unplanned downtime and lowers the overall maintenance costs.
- Accurate temperature and current monitoring help determine when a busbar needs to be serviced or replaced, minimizing the risk of unexpected breakdowns.
- Improved System Reliability
- By continuously monitoring the health of the busbar system, operators can ensure that the power distribution system is running smoothly and efficiently.
- Faults can be identified and rectified before they affect the overall electrical distribution network, enhancing overall system reliability.
- Operational Efficiency
- With real-time data and predictive analytics, the system can help optimize the operation of power systems, ensuring that they operate within safe parameters and at maximum efficiency.
- It helps to ensure that resources are allocated effectively for maintenance, avoiding unnecessary downtime or premature replacements.
- Cost Savings
- Early detection of potential faults reduces the cost of emergency repairs and unplanned shutdowns.
- Predictive maintenance leads to fewer unexpected repairs, lower spare part costs, and a longer lifespan for busbar systems.
- Compliance with Industry Standards
- In many industries, such as power generation, manufacturing, and telecommunications, it is critical to meet safety standards and regulations. A BBT system helps ensure compliance with these standards by providing continuous monitoring and reporting.
Applications of Bus Bar Tracking Systems (BBT)
- Industrial Power Distribution
- Large manufacturing plants, factories, and data centers rely on busbars for distributing power throughout the facility. A BBT helps ensure that these systems remain functional and safe.
- Substations and Power Plants
- Busbars are essential components of electrical substations and power plants. Monitoring busbars in these environments is critical for maintaining the stability and safety of the grid.
- Commercial Buildings
- In large commercial or high-rise buildings, busbars distribute electricity across different floors. BBT can be used to ensure the safe operation of these power systems, preventing costly outages or fire hazards.
- Renewable Energy Systems
- In solar farms or wind energy systems, busbars are used to consolidate the electrical output. A BBT can help monitor the health of these systems, ensuring optimal performance and minimizing downtime.
Key Considerations When Implementing a Bus Bar Tracking System
- System Integration: The BBT system must be integrated into the building or facility’s existing power distribution network, which might require customization depending on the layout and design.
- Scalability: Depending on the size of the installation, the BBT should be scalable to handle multiple busbars or expansion in the future.
- Power Supply: The system must be powered by a reliable source, with backup power options to ensure continuous monitoring during power outages.
- Compliance and Standards: The BBT should be designed in accordance with local electrical safety standards and regulations to ensure that it provides reliable and compliant monitoring.
Conclusion
A Bus Bar Tracking System (BBT) is an essential tool for improving the safety, reliability, and efficiency of electrical power distribution systems. By providing real-time monitoring, fault detection, and predictive maintenance, BBT ensures that busbars—critical components of power distribution—continue to perform safely and efficiently over time.